Invest 30 seconds...
...for what may lead to a life altering association!
Help Line
- +91.8800.2828.00 (IND)
- 1030-1830 Hrs IST, Mon-Sat
- support@expertsglobal.com
...for what may lead to a life altering association!


GMAT is a standardized grad school admission test, conducted over the duration of 3 hours and 7 minutes. The GMAT test essentially consists of 4 distinct sections – Quantitative Reasoning, Verbal Reasoning, Integrated Reasoning (IR), and Analytical Writing Assessment. The total GMAT score is calculated on a range of 200 – 800. The total GMAT score, however, is the scaled score obtained in the Quant and Verbal section, each scored on a range of 6 – 51. The scores obtained in the AWA section, scored on a range of 1 – 6, and in the IR section, scored on a range of 0 – 8, are provided separately and do not add to the total score. Take a free full-length GMAT mock test to understand the GMAT test pattern and structure firsthand.
| Test Section | Number of Questions | Time | Score Range | Mean Scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical Reasoning Assessment (AWA) | 1 | 30 minutes | 0 to 6 (in 0.5 point increment) | 4.48 |
| Integrated Reasoning | 12 | 30 minutes | 1 to 8 (in point 1 increment) | 4.29 |
| Quantitative Reasoning | 31 | 62 minutes | 6 to 51 (in 1 point increment) | 27.04 |
| Verbal Reasoning | 36 | 65 minutes | 6 to 51 (in 1 point increment) | 39.93 |
| Total GMAT Avg. Score | 565 | |||
Source: mba.com
The total GMAT is scored on a range of 200 – 800 points and two-thirds of the test-takers typically score between 400 and 600. The individual sections on GMAT are independently scored on the respective scoring range and the scores obtained in the Verbal and the Quant sections are then scaled to obtain the total GMAT score. Thus, the GMAT Official Score Report consists of 5 parts, namely, the total GMAT score, the Quant score, the Verbal score, the AWA score, and the IR score.
The GMAT Quantitative Reasoning section consists of 31 questions of two types, namely, Data Sufficiency and Problem Solving. The Data Sufficiency questions require you to determine if the provided data is adequate to solve the given problem. Thus, you need to analyze the problem statement and the provided options and determine if
The Problem Solving questions require you to apply the basic rules of arithmetic to solve mathematical problems. Each of the questions on GMAT Quant is graded on a score range of 6 to 51, in 1 point increments.
The GMAT Verbal Reasoning section consists of 36 questions of three types, namely, Reading Comprehension, Sentence Correction, and Critical Reasoning. All these questions are accompanied by multiple choice answers and you need to apply your knowledge of standard English language norms and your ability to read and analyze information to be able to solve these questions. Each of the questions on GMAT Verbal is graded on a score range of 6 to 51, in 1 point increments.
Although GMAT provides the raw section scores, it computes the total GMAT score by scaling the raw Verbal and Quant scores. However, the algorithm for scaling raw scores is not disclosed by GMAT. Thus, it is not possible to determine the particular section scores that will help you obtain your desired total GMAT score. For instance, it is difficult to suggest whether a 45 on Quant will guarantee a 700 on the total GMAT score. The following table plots the GMAT Quant and Verbal raw scores on a 200-point chart:
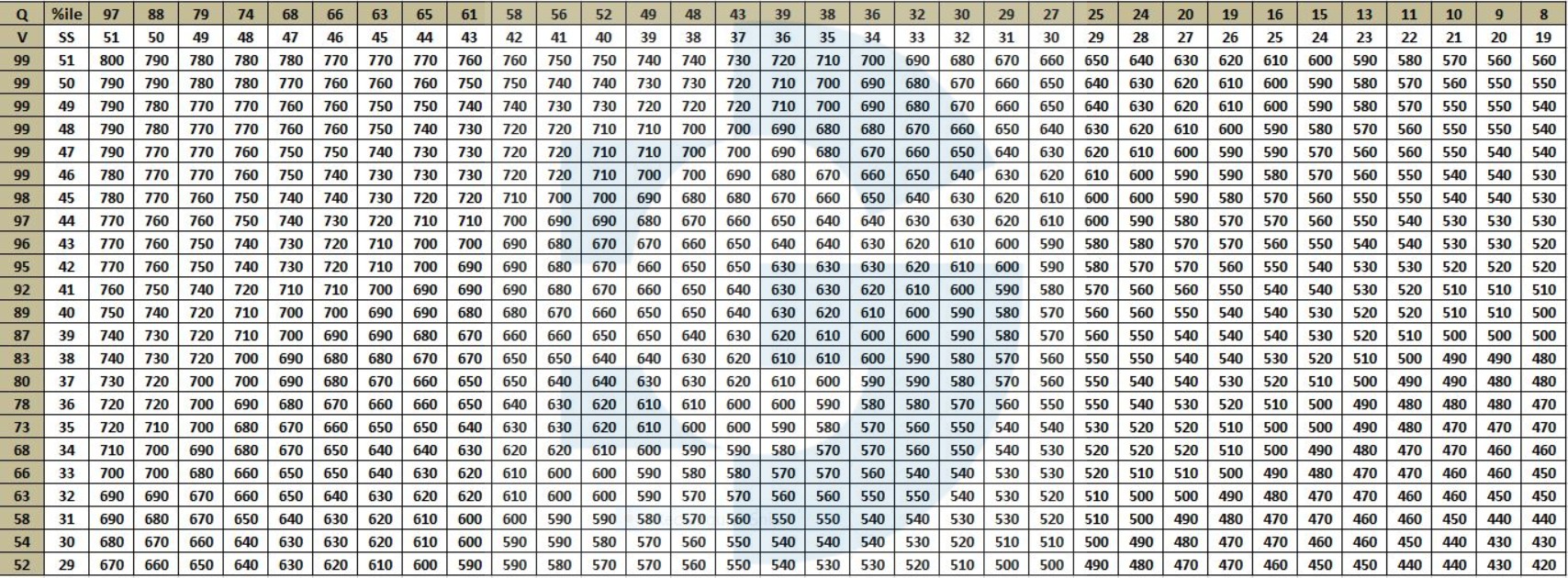
Thus, you can score a 790 on GMAT if
Thus, you can score a 780 on GMAT if
Thus, you can score a 760 on GMAT if
The GMAT AWA section consists of 1 essay – the analysis of an argument. You are required to study a given argument and write a structured essay discussing your inferences of the given argument. A well-composed essay would typically be supported by proper examples and follow the basic syntactical rules of written English language. The GMAT AWA essay is graded on a score range of 0 to 6, in 0.5 point increments. The grading norms are as follows:
The GMAT IR section consists of 12 questions of four types, namely, Graphical Interpretation, Multisource Reasoning, Two-part Analysis, Table Analysis. All these questions are accompanied by multiple choice answers and you need to apply your knowledge of graphs and your ability to work with multiple data to be able to solve these questions. Each of the questions on GMAT IR is graded on a score range of 1 to 8, in 1 point increments.
However, we also need to understand the rationale behind selecting a specific range of numbers as the GMAT score range. The selected GMAT score range is not a random set of numbers, rather, a properly evaluated range of score that helps to maintain consistency of scores. Thus, a GMAT Quant score of 49 in 2000 will represent the same competency as a GMAT Quant score of 49 in 2017, irrespective of the number of changes that the GMAT undergo. GMAT scoring follows a complex algorithm and is a computer-adaptive test sourcing its questions from a large pool of resources to prevent repetition or duplication of questions. Hence, providing a standardized score is of utmost importance. Further, the score ranges do not start from 0, but from 1 or 6. Normally, 0 is a definable number in physical sciences, unlike in educational or psychological sciences. The 0 in the score range for AWA does not indicate performance but the fact that the question was not answered. The scores also need to be adequately precise and should be different from any of the other forms of measurement used to determine test performance. Thus, a score range of 60 – 100 could indicate percentage points or percentiles, the basic determiners of performance. Hence, GMAC has selected the real number range to score each section of GMAT while ensuring that the fundamental performance consistency is maintained throughout and over the years.
Opt for an online GMAT preparation program to make efficient use of your time and resources and familiarize yourself to the GMAT exam format.
Although GMAC does not share the scoring algorithm followed on GMAT, the basic rules for scoring GMAT are as follows:
An exhaustive series of full-length GMAT practice tests will help you practice your time management skills and test-taking strategy.
The GMAT Official Score Report also provides the percentile rank along with the individual scores. A percentile rank shows the proportion of students that you performed better than on GMAT. The percentile rank for each section score as well as the total GMAT score is included in the score report. Although GMAT percentiles do not play an important role in determining your admission to B-schools, it definitely provides an overview of your stand among the pool of applicants. However, while the GMAT scores remain consistent over the years, the GMAT percentile rank will drop with the average GMAT score will increase.
A GMAT score of 760 and above is strong and competitive, a GMAT score of 730 to 750 is brilliant, and a GMAT score below 600 is generally considered weak.
The skills tested on GMAT reportedly are essential to completing your journey of transpiring to a dynamic industry leader. Thus when considering GMAT scores, B-schools do not solely look at the scores but at your ability to reason, solve critical problems, draw inferences, analyze data from multiple sources to derive conclusions, interpret graphs and written instructions, etc. At the same time, your GMAT score is not the only factor that influences the Admission Committee’s decision; it is your profile as a whole – your experience, expertise, knowledge, passion, career goals – that is studied by the Admissions Committee.
The simplest way to determine your ideal GMAT score is to add about 30 points to the average GMAT score requirement stipulated by your dream school. Thus, before you begin your GMAT preparation, set your target GMAT score. For the same, conduct thorough research on the prospective schools you wish to apply to and make a note of their average GMAT score requirement. However, always target the competitive score on GMAT. Refer to the GMAT prep and admissions consulting bundle to be able to obtain expert guidance in completing your MBA admission process.
All the best!